In this review, we will be comparing A120 and Q150, two Passive Bookshelf speakers from JBL and KEF.
Let's have a brief look at the main features
of JBL A120 and KEF Q150 first before getting into our more
detailed comparison.
JBL A120 Key Specs
- 2-way Design
- 1" Hard-Dome Tweeter
- 4.5" Polycellulose Woofer
- 60-40k Hz Frequency Response
- 86 dB Sensitivity
- Impedance: 6ohms
- Power Range:20-125watts
- Weight:3.82kg
- Dimensions (H x W x D): 286.0" x 6-3/4" x 7-7/16"( 286.0 x 172.0 x 189.0mm )
KEF Q150 Key Specs
- 2-way Design
- 11th Generation Uni-Q Driver
- 1" Dome Tweeter
- 5.25" Aluminum Woofer
- 51-28k Hz Frequency Response
- 86 dB Sensitivity
- Impedance: 8ohms
- Power Range:10-100watts
- Weight:5.60kg
- Dimensions (H x W x D): 303.0" x 7.0" x 10.9"( 303.0 x 180.0 x 278.0mm )
What size room are the JBL A120 and KEF Q150 speakers good for?
The size of the room in which you are planning to use these loudspeakers is an important decision
factor. Here we have compared their suitability to various sizes of environments considering their size
and max power parameters:
| Listening Environment* |
JBL A120 |
KEF Q150 |
| Near-field |
Poor |
Average |
| Small Room |
Average |
Good |
| Mid-size Room |
Good |
Average |
| Large Room |
Average |
Poor |
| Very Large Room |
Poor |
Bad |
(* Approximate Room sizes: Small < 100sq. ft / 9 m2,
Mid-size: 100-220 sq. ft / 9-20 m2, Large 220-400 sq. ft / 20-36 m2, Very Large: >
400 sq. ft / 36 m2.
Average Floor Height: 9" / 2.7m. Typical room sizes differ from country to country, and the actual
listening experience changes depending on floor height, room shape, surface materials, listening
position, speaker locations, etc.)
In the following sections, we will get into more detail in order to better understand how the JBL A120 and KEF Q150 compare and hopefully end up with enough arguments to decide which one of these loudspeakers is the better choice for you.
**This post contains affiliate links, and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking
through my links. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Drivers
Both A120 and Q150 are 2-way speakers.
| Driver |
JBL A120 |
KEF Q150 |
|
Driver Setup
|
2-way
|
2-way
|
|
Tweeter
|
1-inch
|
1-inch
|
|
Midrange
|
- |
- |
|
Woofer
|
1 x 4.5-inch
|
1 x 5.25-inch
|
A120 features a 1" aluminum Hard-Dome Tweeter and 1 x 4.5" Polycellulose Woofer . On the other hand, the Q150 features a 1" vented aluminum Dome Tweeter and 1 x 5.25" Aluminum Woofer with a Crossover frequency at 2500Hz.
Frequency Response
A120 has a frequency range of 60-40k Hz whereas Q150 has a frequency range of 51-28k Hz. With a minimum frequency of 51Hz, the Q150 can go significantly deeper on the low side and provide stronger bass compared to the A120's min frequency of 60Hz.
Below graphs depict how these two speakers compare with the max, min and average values of the Min and Max Frequencies of other speakers in the Bookshelf class in our database.
Low Frequency
Bookshelf Speakers
High Frequency
Bookshelf Speakers
None of these speakers achieves full range experience which is commonly agreed as 20Hz-20kHz. In order to achieve lower lows / deeper bass, we recommend you pair these with a subwoofer. Visit our Powered Subwoofers section to find out more about the available options.
Impedance and Sensitivity
A120 is a 6 ohms speaker compared to the Q150 which has a nominal impedance of 8 ohms.
On the other hand, they have the same sensitivity of 86 dBdB.
Sensitivity
Bookshelf Speakers
Power Range
Power
range is the range of input power in watts RMS that a loudspeaker is designed to handle. While using
an amplifier within this range ensures the nominal performance , inputting a power that is higher than the
max wattage can result in a damaged speaker.
A120 can handle a max power of 125 watts RMS from the amp the whereas Q150 has a max power handling value of 100 watts RMS, 25 watts less than the A120.
Keep in mind that a higher max power handling value doesn't necessarily make that a louder speaker
compared to a lower max handling speaker. Loudness or the sound level is also impacted by parameters
such as Impedance, sensitivity and system efficiencies.
Input Type and Bi-Amping / Bi-Wiring
A120 features Post type posts and Q150 has a Post type posts. None of these speakers feature bi-amping/bi-wiring.
 JBL A120's 5-way post terminals
JBL A120's 5-way post terminals
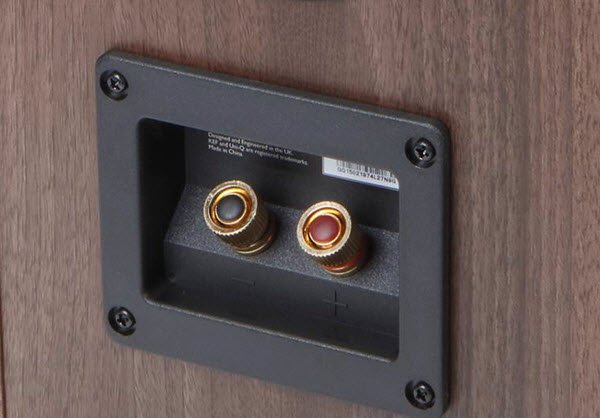 KEF Q150's Post terminals
KEF Q150's Post terminals
Cabinet Type and Port Position
Both A120 and Q150 have rear firing ports. Rear ported speakers generally need more room between the backside of the speaker and the wall compared to sealed and front/bottom ported speakers. Placing the speakers too close to the walls may cause the bass to sound boomy.
If you are limited in space and can't get the speakers away from the backwall, check our Speakers with Front Firing Ports page.
 KEF Q150 Port
KEF Q150 Port
Physical Specs
Size of a speaker can sometimes become an important decision factor due to space constraints or in some cases purely for esthetic reasons. In this section, we are going to compare JBL A120's and KEF Q150's external dimensions. JBL A120 has external dimensions of 286.0 x 172.0 x 189.0mm ( 11-1/4 x 6-3/4 x 7-7/16inch) whereas KEF Q150 has external dimensions of 303.0 x 180.0 x 278.0mm ( 11.9 x 7.0 x 10.9inch) .
KEF Q150 is clearly the larger of the two speakers. Its body is 8mm wider, 17mm taller and 89mm deeper than JBL A120.
Below you can see the front view size comparison of JBL A120 and KEF Q150 in scale.
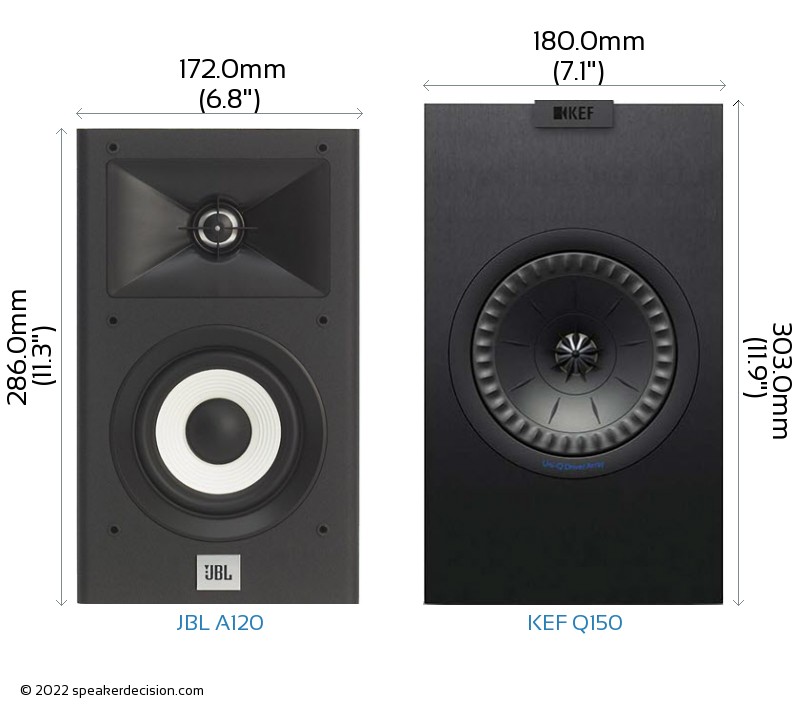 Comparison image of JBL A120 and KEF Q150 Size and External Dimensions
Comparison image of JBL A120 and KEF Q150 Size and External Dimensions
Base Surface Area Comparison
Base surface area of a loudspeaker may become a determining factor when the space in your room or desk is limited.
The base surface area of the JBL A120 is approximately 325.1cm2 / 50.4inch2 and base area of the KEF Q150 is approximately 500.4cm2 / 77.6inch2. The A120 requires 35% less surface area than the Q150 which gives it a small advantage on placement in tight spaces.
Here is an another comparison that shows both speakers on a BDI Octave Media Cabinet, next to a standard size amplifier and turntable in scale:
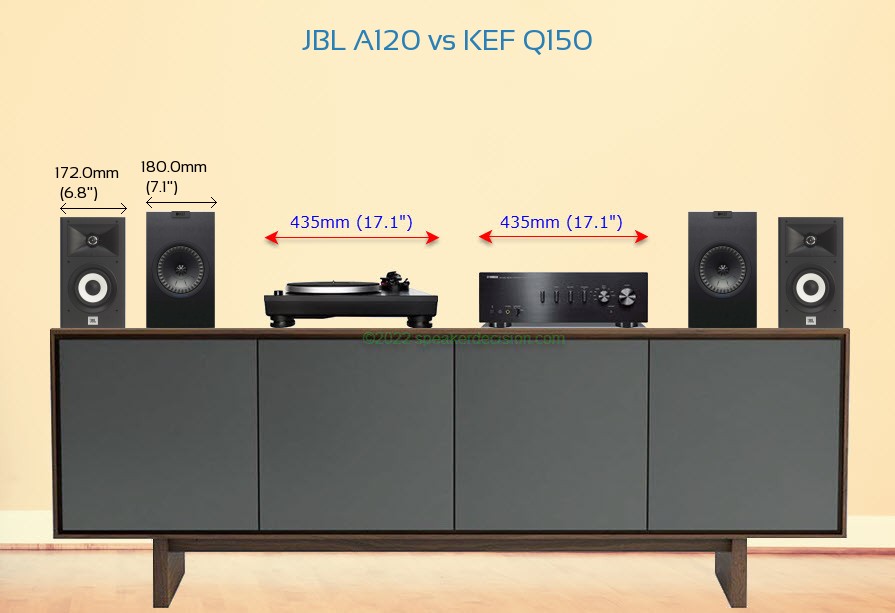 Size Comparison image of JBL A120 and KEF Q150 on a Media Console
Size Comparison image of JBL A120 and KEF Q150 on a Media Console